How Do We Find The Area of Parallelograms, Kites and Trapezoids?
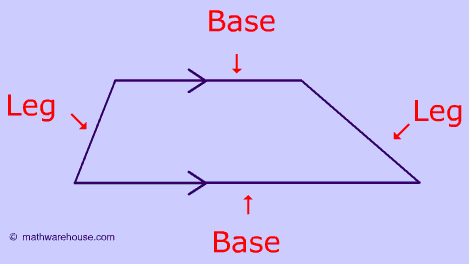
Trapezoid
a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides
Area= (b1+b2)/2(h)
 |
Kites
two pairs of consecutive congruent sides
Area= d1d2/2

 |

 |
| http://www.gotoandplay.it/_articles/2004/07/3dCube/cube.gif
Properties
Solids have properties such as:
-volume (think of how much water it could hold)
- surface area (thinks of the area you would have to paint)
Two types of solids, "polyhedral", and "non-polyhedral"
Polyhedra
They must have flat faces
Prism
Has the same cross section all along it's length
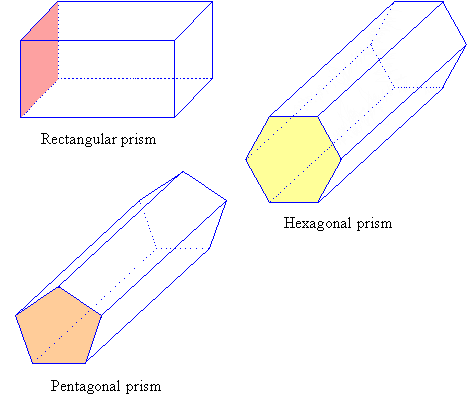
Pyramids

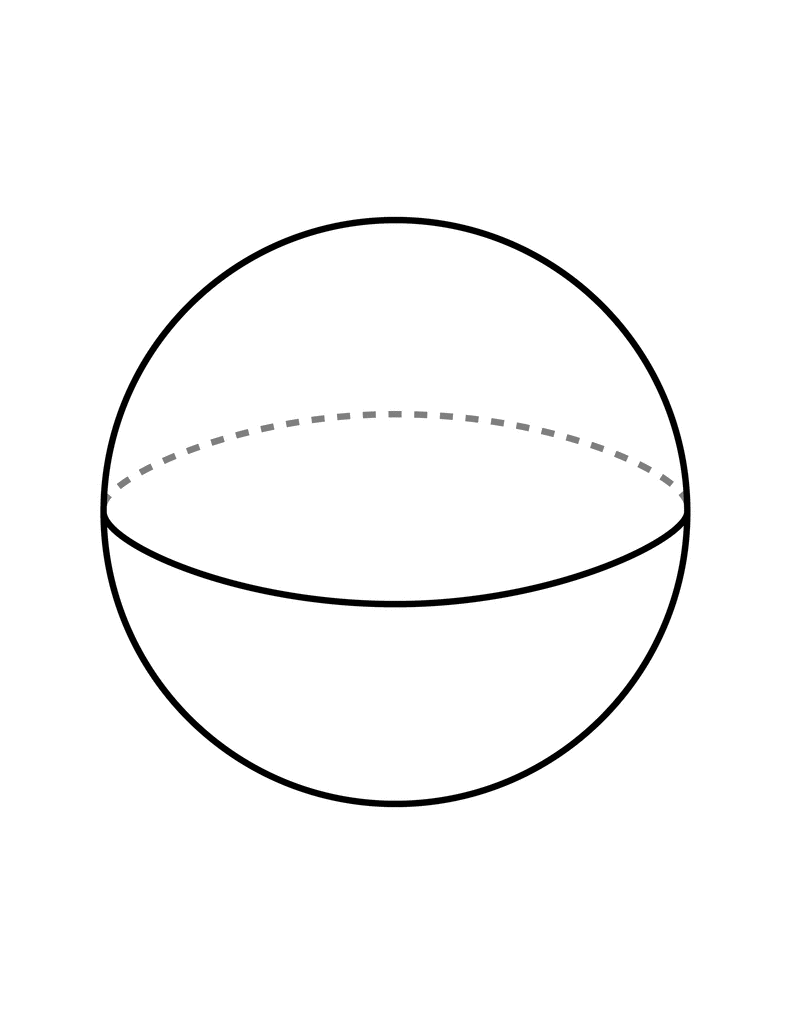
Non- Polyhedra
Any surface that isn't flat
examples:
Sphere
Torus

Cylinders

Cone

Cross sections
The shape you get when cutting straight across an object
Surface Area
Area of the bases + lateral area (area of the sides)
|